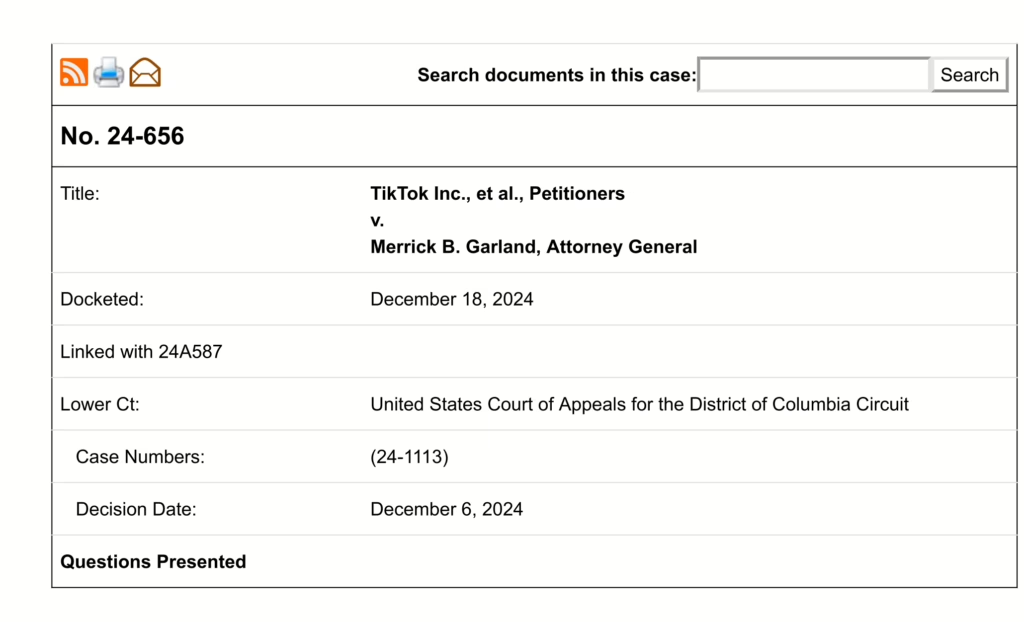
Section 1
All persons born or naturalized in the United States, and subject to the jurisdiction thereof, are citizens of the United States and of the State wherein they reside. No State shall make or enforce any law which shall abridge the privileges or immunities of citizens of the United States; nor shall any State deprive any person of life, liberty, or property, without due process of law; nor deny to any person within its jurisdiction the equal protection of the laws.
This is the section of the 14th Amendment which says that the children of former slaves and former slaves are citizens of the United States.
This needed to be done because before the slaves being freed, they were not citizens. The defeated southern states were investigating how to disenfranchise former slaves.
It was ratified on July 9, 1868.
Text and this Nation’s historical tradition of regulation
When evaluating a modern regulation, when the Constitutions plain text covers an individual’s conduct, the Constitution presumptively protects that conduct.
In this case, “Is the child of an illegal alien born in the United States a United States citizen?”
The plain text of the Constitution clearly covers the individual’s conduct, becoming or acting as a US Citizen.
Since the plain text covers the conduct, the government must demonstrate that the regulation is consistent with this Nation’s historical tradition of regulation.
What is the regulation?
Sec. 2. Policy. (a) It is the policy of the United States that no department or agency of the United States government shall issue documents recognizing United States citizenship, or accept documents issued by State, local, or other governments or authorities purporting to recognize United States citizenship, to persons: (1) when that person’s mother was unlawfully present in the United States and the person’s father was not a United States citizen or lawful permanent resident at the time of said person’s birth, or (2) when that person’s mother’s presence in the United States was lawful but temporary, and the person’s father was not a United States citizen or lawful permanent resident at the time of said person’s birth.
— Protecting the Meaning and Value of American Citizenship, Executive Order, whitehouse.gov
This is fairly simple. You are a US Citizen if your mother or father is a US Citizen. You are a US Citizen if your mother or father is a lawful permanent resident when you are born.
Being whelped on US grounds does not make you a citizen.
Is this interpretation consistent with giving former slaves citizenship?
Yes. Former slaves were naturalized (I Believe). So they were citizens.
Their children were born to citizens or lawful permanent residents.
What does “and subject to the jurisdiction thereof” mean?
We know what it meant in 1898. In March of that year, the Supreme Court issued their opinion in —United States V. Wong Kim Ark, 169 U.S. 649 (1898). This is barely 30 years from the ratification of the Amendment.
Wong Kim Ark was the child of Chinese parents. Those parents were NOT naturalized and were subjects of the Emperor of China.
When Wong Kim was 17 years old, he took a trip to China. He returned with no issues. He claimed to be a US Citizen.
In 1894, four years later, he took another trip to China. This time, when he returned, he was not allowed to disembark. Instead, he was detained.
The District Court for the Northern District of California found that Wong Kim Ark was a US citizen by virtue of his birth and had him released. The government appealed to the Supreme Court.
The question presented by the record is whether a child born in the United States, of parents of Chinese descent, who, at the time of his birth, are subjects of the Emperor of China, but have a permanent domicil and residence in the United States, and are there carrying on business, and are not employed in any diplomatic or official capacity under the Emperor of China, becomes at the time of his birth a citizen of the United States, by virtue of the first clause of the Fourteenth Amendment of the Constitution, “All persons born or naturalized in the United States, and subject to the jurisdiction thereof, are citizens of the United States and of the State wherein they reside.”
—id.
This is preciously the question the new EO brings forth.
In construing any act of legislation, whether a statute enacted by the legislature, or a constitution established by the people as the supreme law of the land, regard is to be had, not only to all parts of the act itself, and of any former act of the same law-making power, of which the act in question is an amendment; but also to the condition, and to the history, of the law as previously existing, and in the light of which the new act must be read and interpreted.
—id.
That’s old time speak for “plain text” and “historical tradition of regulation”.
To create allegiance by birth, the party must be born, not only within the territory, but within the ligeance of the government. If a portion of the country be taken and held by conquest in war, the conqueror acquires the rights of the conquered as to its dominion and government, and children born in the armies of a State, while abroad and occupying a foreign country, are deemed to be born in the allegiance of the sovereign to whom the army belongs.
—id. quoting Chancellor Kent, Kent Com. (6th ed.) 39, 42
So a child must be born not only within the country, but within the “ligeance” of the country. If they are born of an occupying entity, then they are citizens of the occupying entity, not the country within which they are born.
The real object of the Fourteenth Amendment of the Constitution, in qualifying the words, “All persons born in the United States,” by the addition, “and subject to the jurisdiction thereof,” would appear to have been to exclude, by the fewest and fittest words, (besides children of members of the Indian tribes, standing in a peculiar relation to the National Government, unknown to the common law,) the two classes of cases children born of alien enemies in hostile occupation, and children of diplomatic representatives of a foreign State both of which, as has already been shown, by the law of England, and by our own law, from the time of the first settlement of the English colonies in America, had been recognized exceptions to the fundamental rule of citizenship by birth within the country. Calvin’s Case, 7 Rep. 1, 18b; Cockburn on Nationality, 7; Dicey Conflict of Laws, 177; Inglis v. Sailors’ Snug Harbor, 3 Pet. 99, 155; 2 Kent Com. 39, 42.
—id.
Upon the facts agreed in this case, the American citizenship which Wong Kim Ark acquired by birth within the United States has not been lost or taken away by anything happening since his birth. No doubt he might himself, after coming of age, renounce this citizenship, and become a citizen of the country of his parents, or of any other country;
—id.
When everything is said, the Supreme Court in 1898 found that if you were born of parents that were here legally, you were an American citizen.
Is that the end?
Not really, the issues are that of an invading force, or people that are here illegally. Do they have the same birth right as a child born of people here legally?
There is a strong argument to be made that illegal aliens do not gift their whelp with American citizenship merely by pushing them out while on US soil.
It is clear that if they were members of an invading army, their children would not be American citizens.
Standing
Mr. Wong Kim Ark was a person who claimed to be a US Citizen by birth. When the state refused him entrance to the United States, he was able to file a case arguing that he was a citizen and should be granted internee.
The state argued against him.
This means that Wong Kim had standing. The case was about him.
Now consider the current situation. Jose sneaks across the border with his wife Maria. Maria got knocked up by somebody, either north or south of the border, it doesn’t matter.
Maria and Jose show up at the hospital emergency room, where they are given “free” health care because they have no intention of paying for it.
Maria whelps Jose Jr.
Jose and Maria are handed a birth certificate for Junior. They are told they are the proud parents of an American Citizen.
You’re in the next bed and you hear that another illegal has their anchor baby.
You file suit claiming that the Fourteenth Amendment doesn’t grant citizenship to foreign invaders.
The case is dismissed. You have no standing.
This is correct.
Who has standing?
The child, the parents, and the state.
If the state isn’t challenging the granting of citizenship and the parents are not, and the child isn’t, then there is no suit.
What does the EO change?
The EO says that if you are not here legally, whelping a child here doesn’t grant that child citizenship.
If Jose wants Junior to be a citizen, he needs to file suit. The state can now argue against birthright for invaders.
If Jose loses, he better stop. If he appeals, then the circuit court will hear the case. And the state will again argue invaders don’t get to make citizens.
If the loser of that case appeals again, it will be before the Supreme Court.
At which point we will have our second opinion on birthright citizenship being granted by the 14th. It might not turn out the way that the left thinks it should.